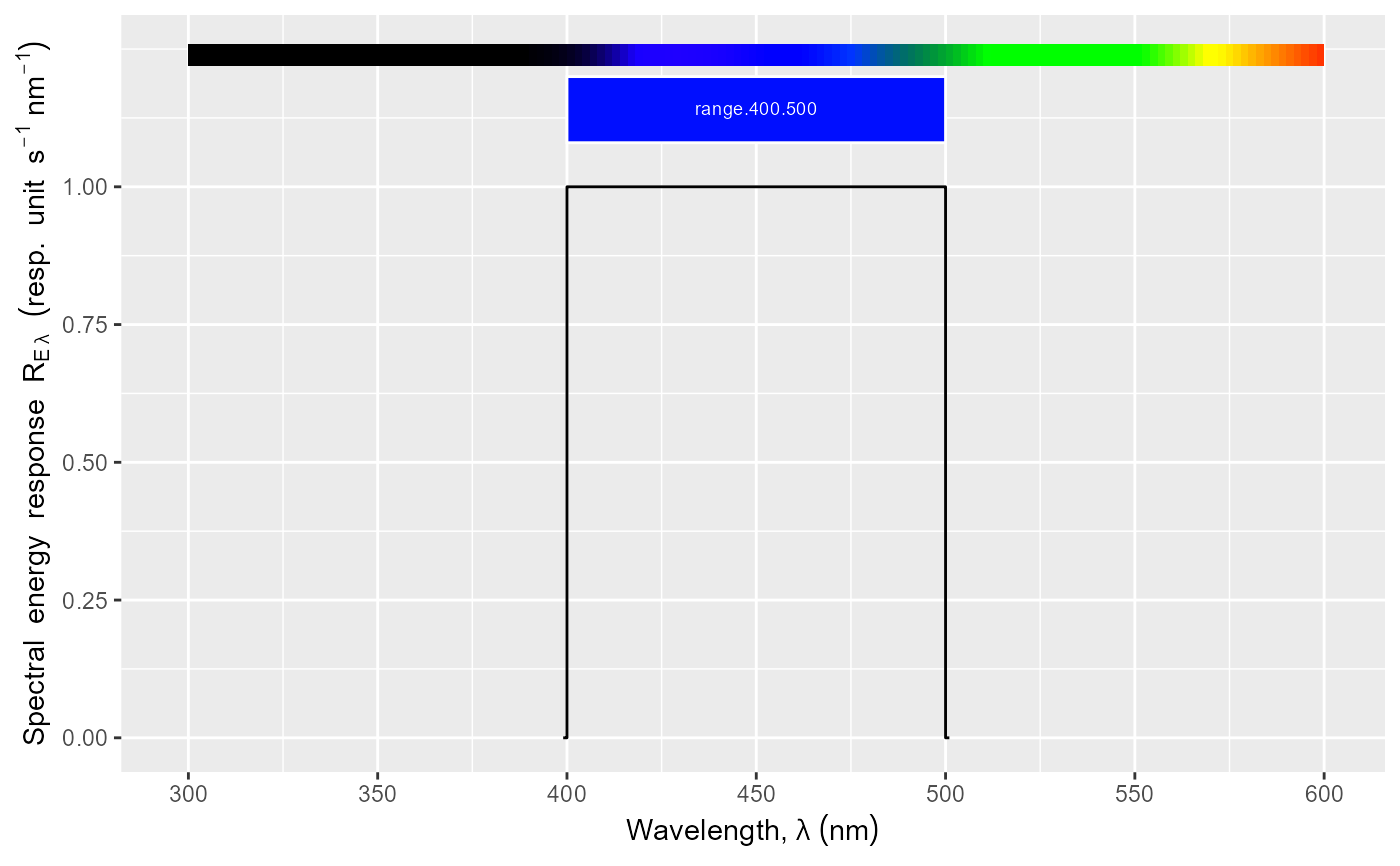
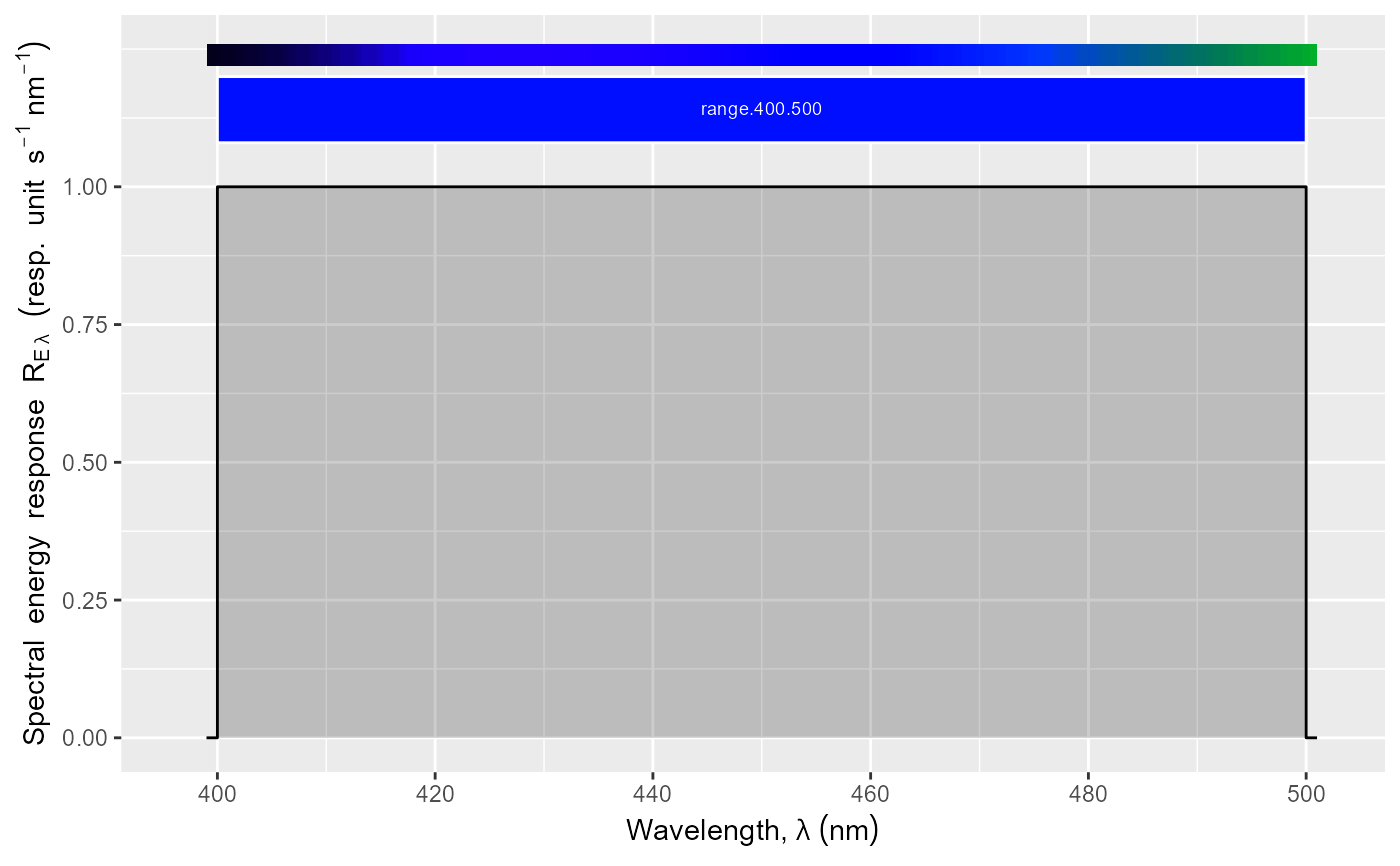
Create a complete ggplot for a waveband descriptor.
Source:R/autoplot-waveband.R
autoplot.waveband.RdConstruct a ggplot object with an annotated plot of a waveband object.
Usage
# S3 method for class 'waveband'
autoplot(
object,
...,
w.length = NULL,
range = NULL,
fill = 0,
span = NULL,
wls.target = "HM",
unit.in = getOption("photobiology.radiation.unit", default = "energy"),
unit.out = unit.in,
annotations = NULL,
by.group = FALSE,
geom = "line",
wb.trim = TRUE,
norm = NA,
text.size = 2.5,
ylim = c(NA, NA),
object.label = deparse(substitute(object)),
na.rm = TRUE
)Arguments
- object
a waveband object.
- ...
arguments passed along by name to
autoplot.response_spct().- w.length
numeric vector of wavelengths (nm).
- range
an R object on which range() returns a vector of length 2, with min annd max wavelengths (nm).
- fill
value to use as response for wavelengths outside the waveband range.
- span
a peak is defined as an element in a sequence which is greater than all other elements within a window of width span centered at that element.
- wls.target
numeric vector indicating the spectral quantity values for which wavelengths are to be searched and interpolated if need. The
characterstrings "half.maximum" and "half.range" are also accepted as arguments. A list withnumericand/orcharactervalues is also accepted.- unit.in, unit.out
the type of unit we assume as reference: "energy" or "photon" based for the waveband definition and the implicit matching response plotted.
- annotations
a character vector. For details please see section Plot Annotations.
- by.group
logical flag If TRUE repeated identical annotation layers are added for each group within a plot panel as needed for animation. If
FALSE, the default, single layers are added per panel.- geom
character The name of a ggplot geometry, currently only
"area","spct"and"line".- wb.trim
logical. Passed to
trim_wl. Relevant only when thewavebandextends partly outsiderange.- norm
numeric or character Normalization wavelength (nm) or character string
"max"or other criterion for normalization.- text.size
numeric size of text in the plot decorations.
- ylim
numeric y axis limits,
- object.label
character The name of the object being plotted.
- na.rm
logical.
Details
A response_spct object is created based on the
waveband object and the argument passed to parameter w.length.
By default wavelengths spanning the waveband definition expanded by
1 nm at each end are used. A waveband object can describe either a
simple wavelength range or a (biological) spectral weighting function
(BSWF). An effectiveness is a response expressed per unit of excitation,
and in most cases normalised.
Effectiveness spectra can be plotted expressing the spectral effectiveness
either per mol of photons (\(1 mol^{-1} nm\)) or per joule of energy
(\(1 J^{-1} nm\)), selected through formal argument unit.out. The
value of unit.in has no direct effect on the result for BSWFs,
as BSWFs are defined based on a certain base of expression, which is
enforced. Indirectly it affects plots as unit.out defaults to
unit.in. In contrast, for wavebands which only define a wavelength
range, changing the assumed reference irradiance units, changes the
responsivity according to Plank's law, i.e., the four possible combinations
of pairs of values for unit.in and unit.out produce four
different plots. _Only in rare cases unit.in and unit.out
is useful as normally the dependency on base of expresion is encoded in
the waveband definition as a BSWF._
While w.length` provides the wavelengths of the generated
response spectrum, `range` sets the wavelength range of the \(x\)-axis
of the plot.
Unused named arguments are forwarded to
autoplot.response_spct(), allowing control of additional plot
properties.
Plot Annotations
The recognized annotation names are: "summaries", "peaks",
"peak.labels", "valleys", "valley.labels",
"wls", "wls.labels", "colour.guide",
"color.guide", "boxes", "segments", "labels".
In addition, "+" is interpreted as a request to add to the already
present default annotations, "-" as request to remove annotations
and "=" or missing"+" and "-" as a request to reset
annotations to those requested. If used, "+", "-" or
"=" must be the first member of a character vector, and followed by
one or more of the names given above. To simultaneously add and remove
annotations one can pass a list containing character vectors
each assembled as described. The vectors are applied in the order they
appear in the list. To disable all annotations pass "" or
c("=", "") as argument. Adding a variation of an annotation already
present, replaces the existing one automatically: e.g., adding
"peak.labels" replaces"peaks" if present.
The annotation layers are added to the plot using statistics defined in 'ggspectra':
stat_peaks, stat_valleys,
stat_label_peaks, stat_label_valleys,
stat_find_wls, stat_spikes,
stat_wb_total, stat_wb_mean,
stat_wb_irrad, stat_wb_sirrad,
stat_wb_contribution, stat_wb_relative,
and stat_wl_strip. However, only some of their parameters
can be passed arguments through autoplot methods. In some cases
the defaults used by autoplot methods are not the defaults of the
statistics.
See also
autoplot.response_spct,
waveband.
Other autoplot methods:
autoplot.calibration_spct(),
autoplot.cps_spct(),
autoplot.filter_spct(),
autoplot.object_spct(),
autoplot.raw_spct(),
autoplot.reflector_spct(),
autoplot.response_spct(),
autoplot.source_spct()