stat_peaks finds at which x positions the global y maximun or local
y maxima are located. stat_valleys finds at which x positions the
global y minimum or local y minima located. They both support filtering
of relevant peaks. Axis flipping is currently not supported.
Usage
stat_peaks(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
geom = "point",
position = "identity",
...,
span = 5,
global.threshold = 0.01,
local.threshold = NULL,
local.reference = "median",
strict = FALSE,
refine.wl = FALSE,
method = "spline",
chroma.type = "CMF",
label.fmt = "%.3g",
x.label.fmt = label.fmt,
y.label.fmt = label.fmt,
x.label.transform = function(x) {
x
},
y.label.transform = function(x) {
x
},
x.colour.transform = x.label.transform,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = FALSE,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)
stat_valleys(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
geom = "point",
position = "identity",
...,
span = 5,
global.threshold = -0.99,
local.threshold = NULL,
local.reference = "median",
strict = FALSE,
refine.wl = FALSE,
method = "spline",
chroma.type = "CMF",
label.fmt = "%.3g",
x.label.fmt = label.fmt,
y.label.fmt = label.fmt,
x.label.transform = function(x) {
x
},
y.label.transform = function(x) {
x
},
x.colour.transform = x.label.transform,
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = FALSE,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)Arguments
- mapping
The aesthetic mapping, usually constructed with
aesoraes_. Only needs to be set at the layer level if you are overriding the plot defaults.- data
A layer specific dataset - only needed if you want to override the plot defaults.
- geom
The geometric object to use display the data
- position
The position adjustment to use for overlapping points on this layer
- ...
other arguments passed on to
layer. This can include aesthetics whose values you want to set, not map. Seelayerfor more details.- span
odd positive integer A peak is defined as an element in a sequence which is greater than all other elements within a moving window of width
spancentred at that element. The default value is 5, meaning that a peak is taller than its four nearest neighbours.span = NULLextends the span to the whole length ofx.- global.threshold
numeric A value belonging to class
"AsIs"is interpreted as an absolute minimum height or depth expressed in data units. A barenumericvalue (normally between 0.0 and 1.0), is interpreted as relative tothreshold.range. In both cases it sets a global height (depth) threshold below which peaks (valleys) are ignored. A bare negativenumericvalue indicates the global height (depth) threshold below which peaks (valleys) are be ignored. Ifglobal.threshold = NULL, no threshold is applied and all peaks returned.- local.threshold
numeric A value belonging to class
"AsIs"is interpreted as an absolute minimum height (depth) expressed in data units relative to a within-window computed reference value. A barenumericvalue (normally between 0.0 and 1.0), is interpreted as expressed in units relative tothreshold.range. In both caseslocal.thresholdsets a local height (depth) threshold below which peaks (valleys) are ignored. Iflocal.threshold = NULLor ifspanspans the whole ofx, no threshold is applied.- local.reference
character One of
"median","median.log","median.sqrt","farthest","farthest.log"or"farthest.sqrt". The reference used to assess the height of the peak, either the minimum/maximum value within the window or the median of all values in the window.- strict
logical flag: if
TRUE, an element must be strictly greater than all other values in its window to be considered a peak.- refine.wl
logical Flag indicating if peak or valleys locations should be refined by fitting a function.
- method
character String with the name of a method used for peak fitting. Currently only spline interpolation is implemented.
- chroma.type
character one of "CMF" (color matching function) or "CC" (color coordinates) or a
chroma_spctobject.- label.fmt, x.label.fmt, y.label.fmt
character strings giving a format definition for construction of character strings labels with function
sprintffromxand/oryvalues.- x.label.transform, y.label.transform, x.colour.transform
function Applied to
xoryvalues when constructing the character labels or computing matching colours.- na.rm
a logical value indicating whether NA values should be stripped before the computation proceeds.
- show.legend
logical. Should this layer be included in the legends?
NA, the default, includes if any aesthetics are mapped.FALSEnever includes, andTRUEalways includes.- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics, rather than combining with them. This is most useful for helper functions that define both data and aesthetics and shouldn't inherit behaviour from the default plot specification, e.g.borders.
Value
A data frame with one row for each peak (or valley) found in the
data. If refine.wl = FALSE, the returned rows have x and
y matching those in a row in the input data. If
refine.wl = TRUE, interpolation based on a fitted spline is used to
compute new x and y values.
Details
These stats use geom_point by default as it is the geom most
likely to work well in almost any situation without need of tweaking. The
default aesthetics set by these stats allow their direct use with
geom_text, geom_label, geom_line, geom_rug,
geom_hline and geom_vline. The formatting of the labels
returned can be controlled by the user.
Two tests make it possible to ignore irrelevant peaks or valleys. One test
controlled by (global.threshold) is based on the absolute
height/depth of peaks/valleys and can be used in all cases to ignore
globally low peaks and shallow valleys. A second test controlled by
(local.threshold) is available when the window defined by `span`
does not include all observations and can be used to ignore peaks/valleys
that are not locally prominent. In this second approach the height/depth of
each peak/valley is compared to a summary computed from other values within
the window where it was found. In this second case, the reference value
used is the summary indicated by local.reference. The values
global.threshold and local.threshold if bare numeric are
relative to the range of y. Thresholds for ignoring too small peaks
are applied after peaks are searched for, and threshold values can in some
cases result in no peaks being displayed.
Note
Parameter ignore_threshold was renamed global.threshold
in version 0.3.16.
These stats work nicely together with geoms geom_text_repel and
geom_label_repel from package ggrepel to
solve the problem of overlapping labels
by displacing them. To discard overlapping labels use check_overlap =
TRUE as argument to geom_text.
By default the labels are character values ready to be added as is, but
with a suitable label.fmt labels suitable for parsing by the geoms
(e.g. into expressions containing Greek letters or super or subscripts) can
be also easily obtained.
Computed and copied variables in the returned data frame
- x
x-value at the peak (or valley) as numeric
- y
y-value at the peak (or valley) as numeric
- x.label
x-value at the peak (or valley) formatted as character
- y.label
y-value at the peak (or valley) formatted as character
- wl.color
color definition calculated by assuming that x-values are wavelengths expressed in nanometres.
- BW.color
color definition, either "black" or "white", as needed to ensure high contrast to
wl.color.
Default aesthetics
Set by the statistic and available to geoms.
- label
stat(x.label)
- xintercept
stat(x)
- yintercept
stat(y)
- fill
stat(wl.color)
Required aesthetics
Required by the statistic and need to be set with aes().
- x
numeric, wavelength in nanometres
- y
numeric, a spectral quantity
See also
find_peaks, which is used internally.
Other stats functions:
stat_color(),
stat_find_qtys(),
stat_find_wls(),
stat_label_peaks(),
stat_spikes(),
stat_wb_box(),
stat_wb_column(),
stat_wb_contribution(),
stat_wb_hbar(),
stat_wb_irrad(),
stat_wb_label(),
stat_wb_mean(),
stat_wb_relative(),
stat_wb_sirrad(),
stat_wb_total(),
stat_wl_strip(),
stat_wl_summary()
Examples
# ggplot() methods for spectral objects set a default mapping for x and y.
# PEAKS
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks()
 # threshold relative to data range [0..1]
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(global.threshold = 0.6) # 0.6 * range of data
# threshold relative to data range [0..1]
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(global.threshold = 0.6) # 0.6 * range of data
 # threshold in data units
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(global.threshold = I(0.4))
# threshold in data units
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(global.threshold = I(0.4))
 # threshold in data units
ggplot(sun.spct, unit.out = "photon") +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(global.threshold = I(2e-6)) # Q in mol m-2 s-1
# threshold in data units
ggplot(sun.spct, unit.out = "photon") +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(global.threshold = I(2e-6)) # Q in mol m-2 s-1
 # VALLEYS
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_valleys()
# VALLEYS
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_valleys()
 # discard multiple maxima or minima
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_valleys(strict = TRUE)
# discard multiple maxima or minima
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_valleys(strict = TRUE)
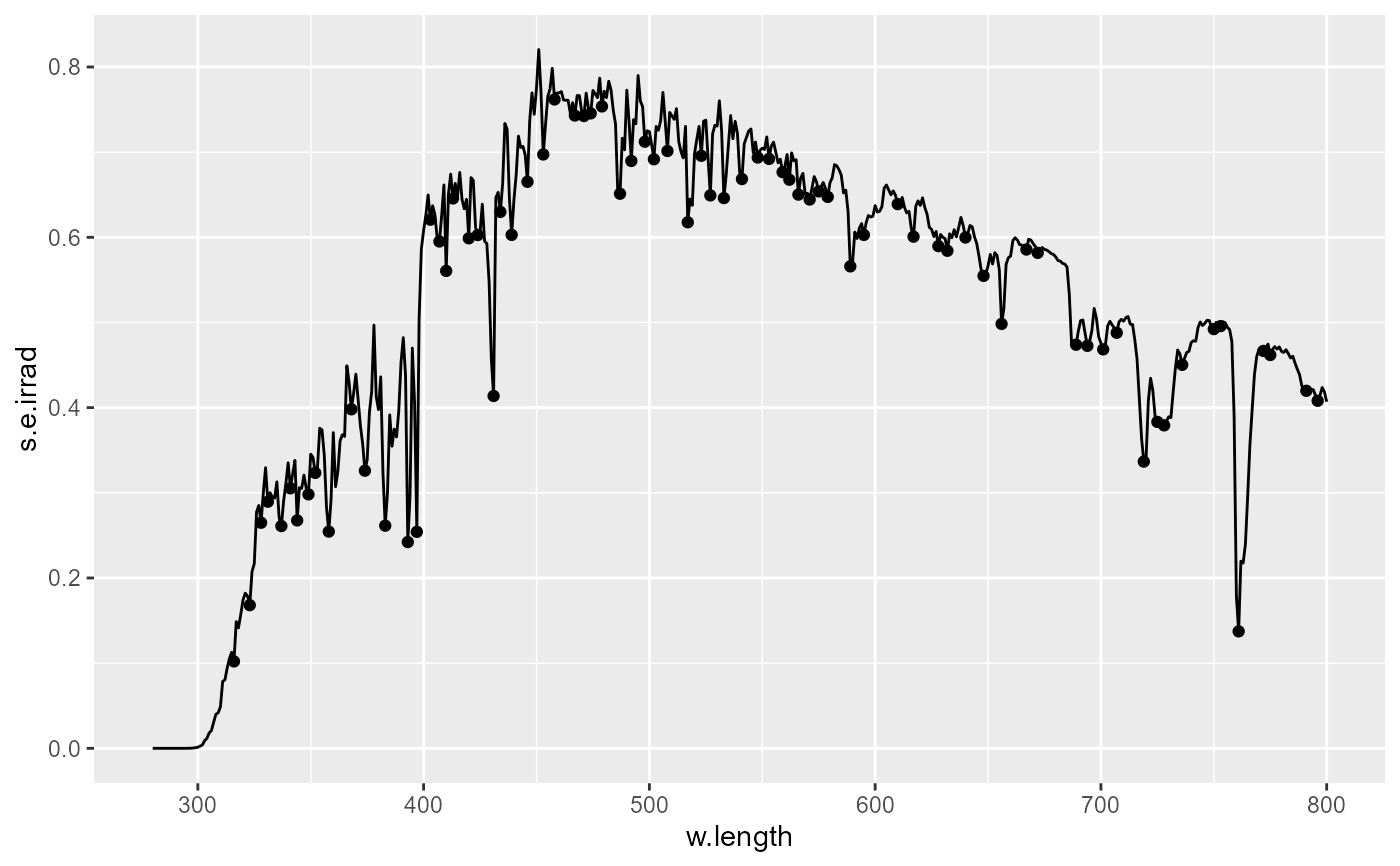 # threshold relative to data range [0..1]
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_valleys(global.threshold = 0.6)
# threshold relative to data range [0..1]
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_valleys(global.threshold = 0.6)
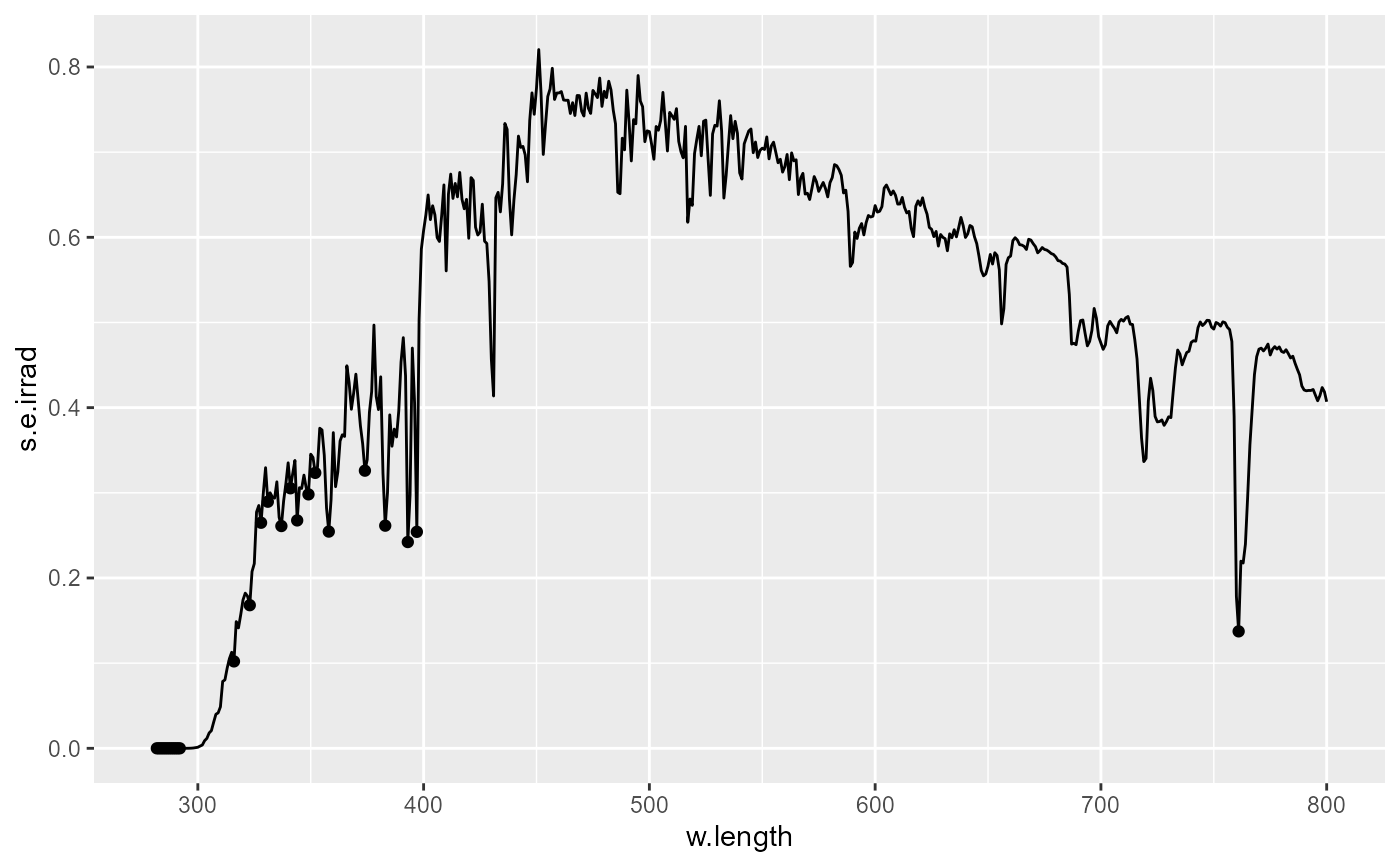 # reverse threshold relative to data range [-1..0]
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_valleys(global.threshold = -0.9)
# reverse threshold relative to data range [-1..0]
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_valleys(global.threshold = -0.9)
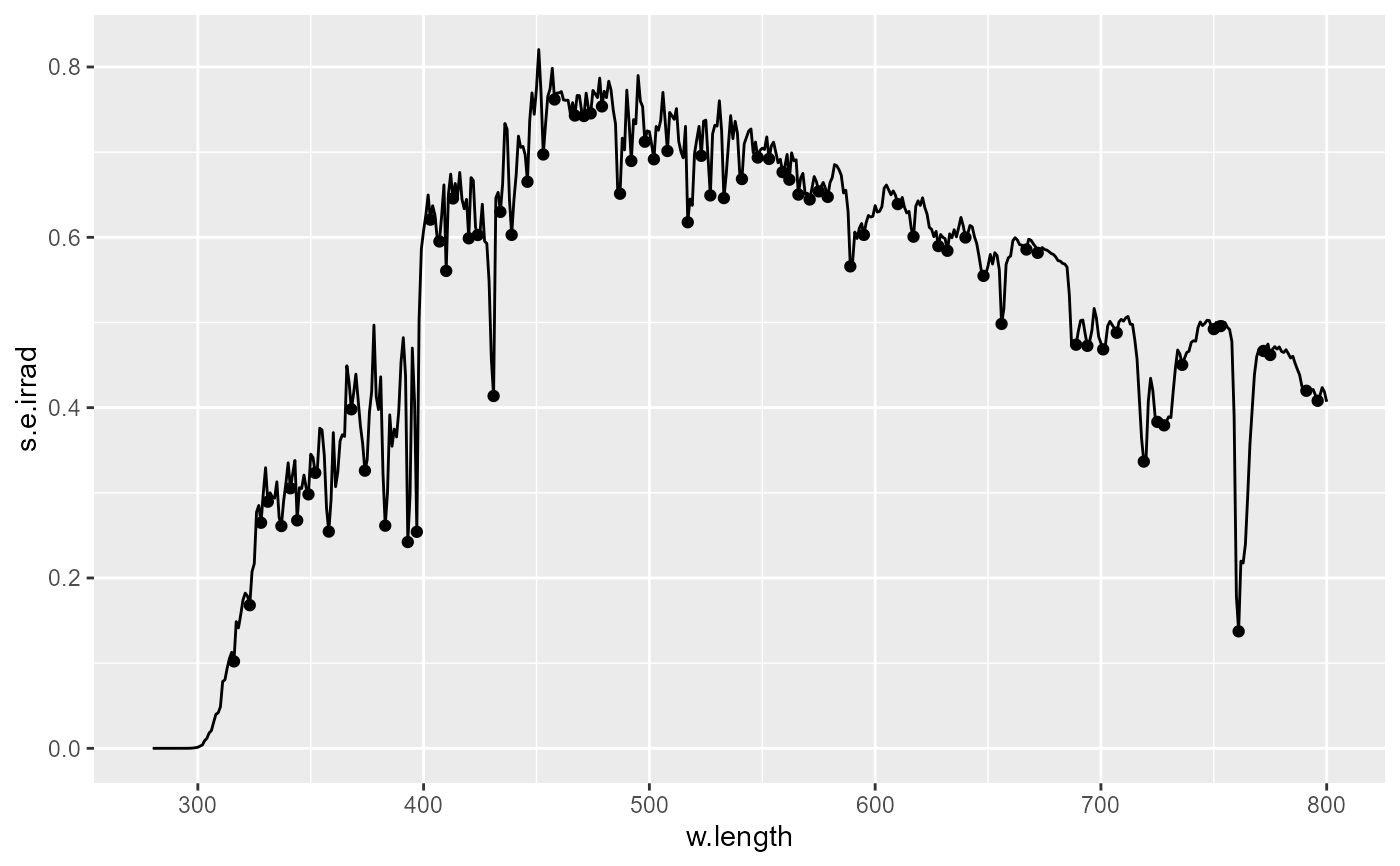 # threshold in data units using I()
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_valleys(global.threshold = I(0.6), strict = TRUE)
# threshold in data units using I()
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_valleys(global.threshold = I(0.6), strict = TRUE)
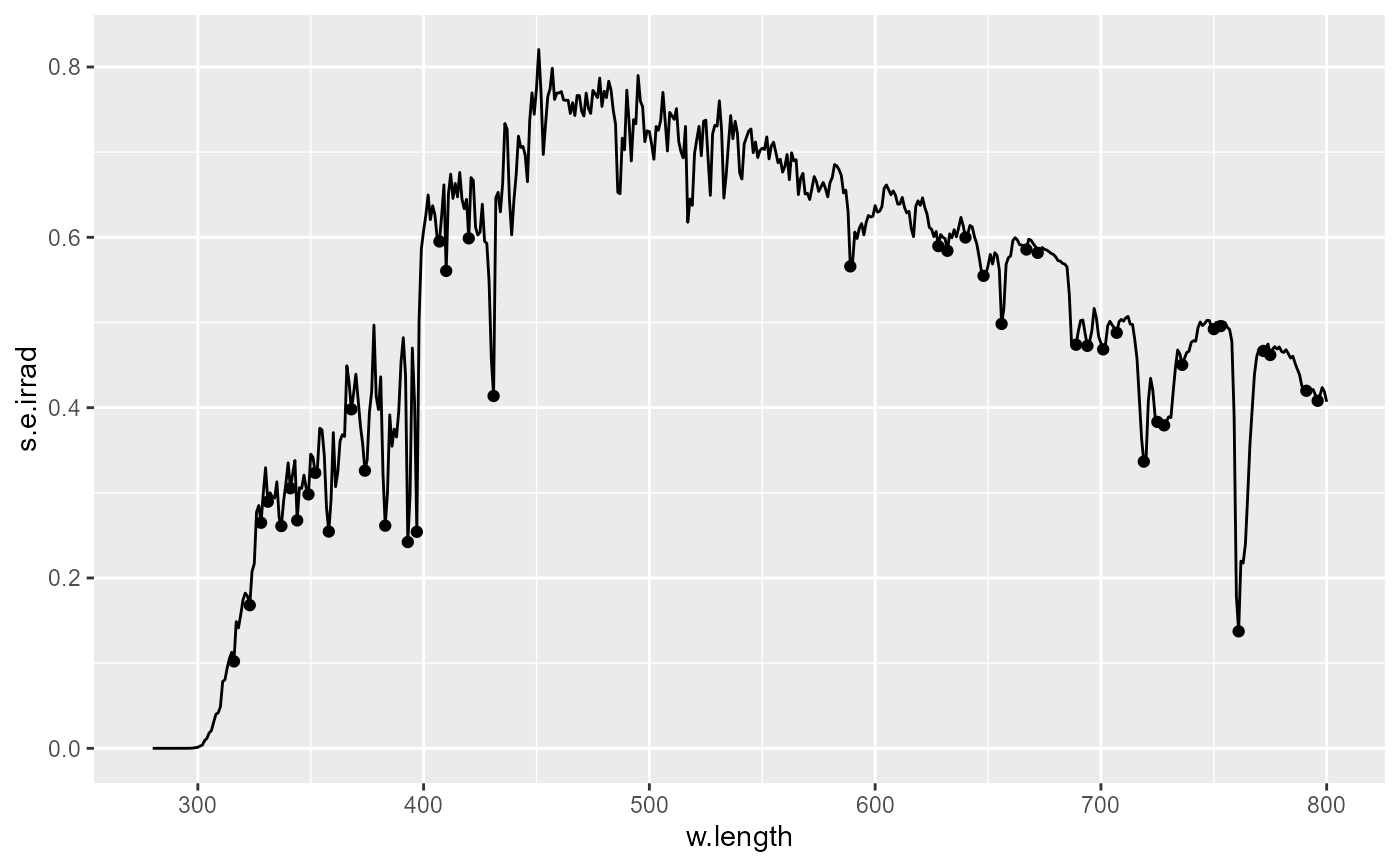 # USING OTHER COMPUTED VALUES
# colours matching the wavelength at peaks
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(span = 51, size = 2.7,
mapping = aes(colour = after_stat(wl.colour))) +
scale_color_identity()
# USING OTHER COMPUTED VALUES
# colours matching the wavelength at peaks
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(span = 51, size = 2.7,
mapping = aes(colour = after_stat(wl.colour))) +
scale_color_identity()
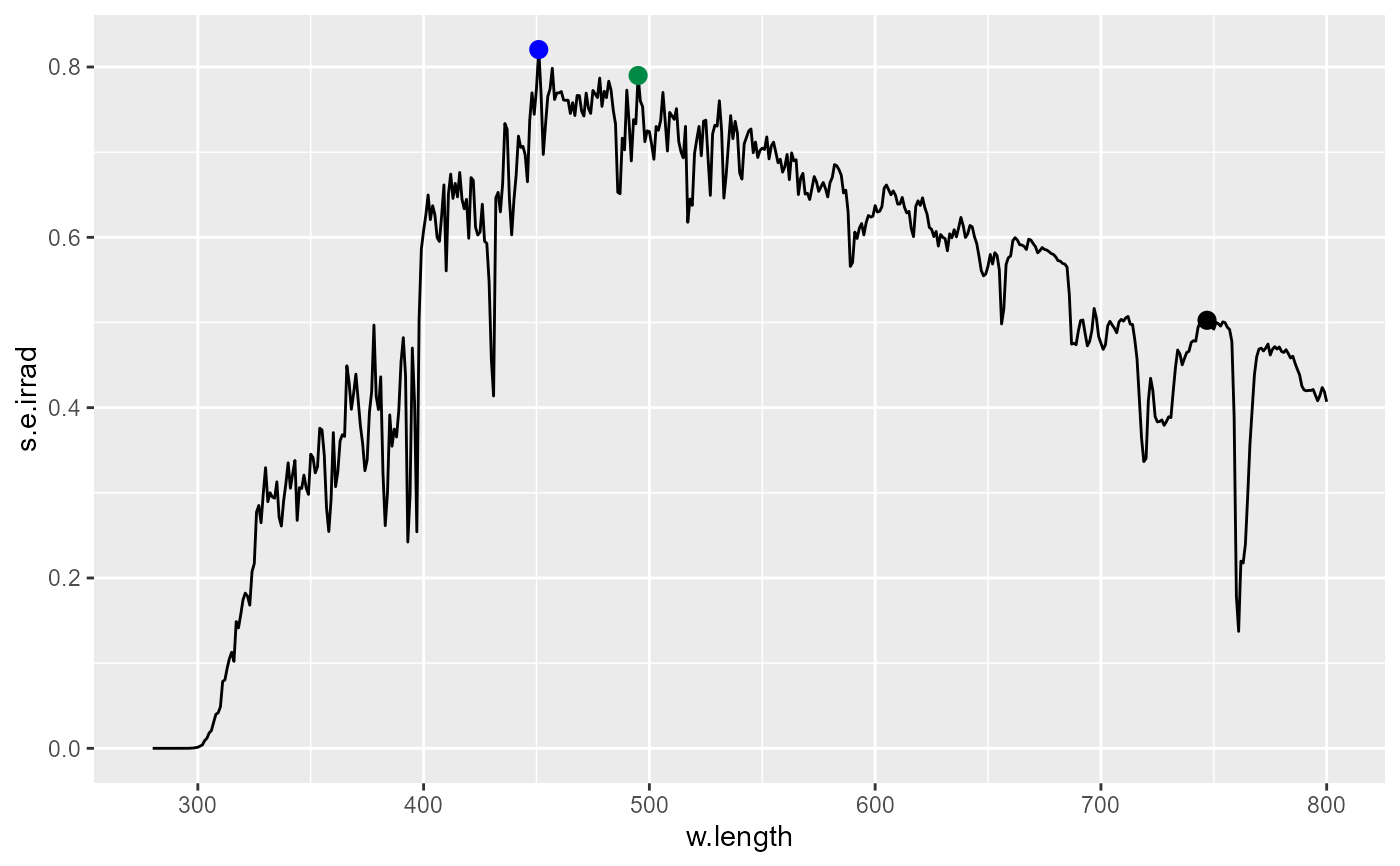 # labels for local maxima
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(span = 51, geom = "point", colour = "red") +
stat_peaks(span = 51, geom = "text", colour = "red",
vjust = -0.4, label.fmt = "%3.2f nm")
# labels for local maxima
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(span = 51, geom = "point", colour = "red") +
stat_peaks(span = 51, geom = "text", colour = "red",
vjust = -0.4, label.fmt = "%3.2f nm")
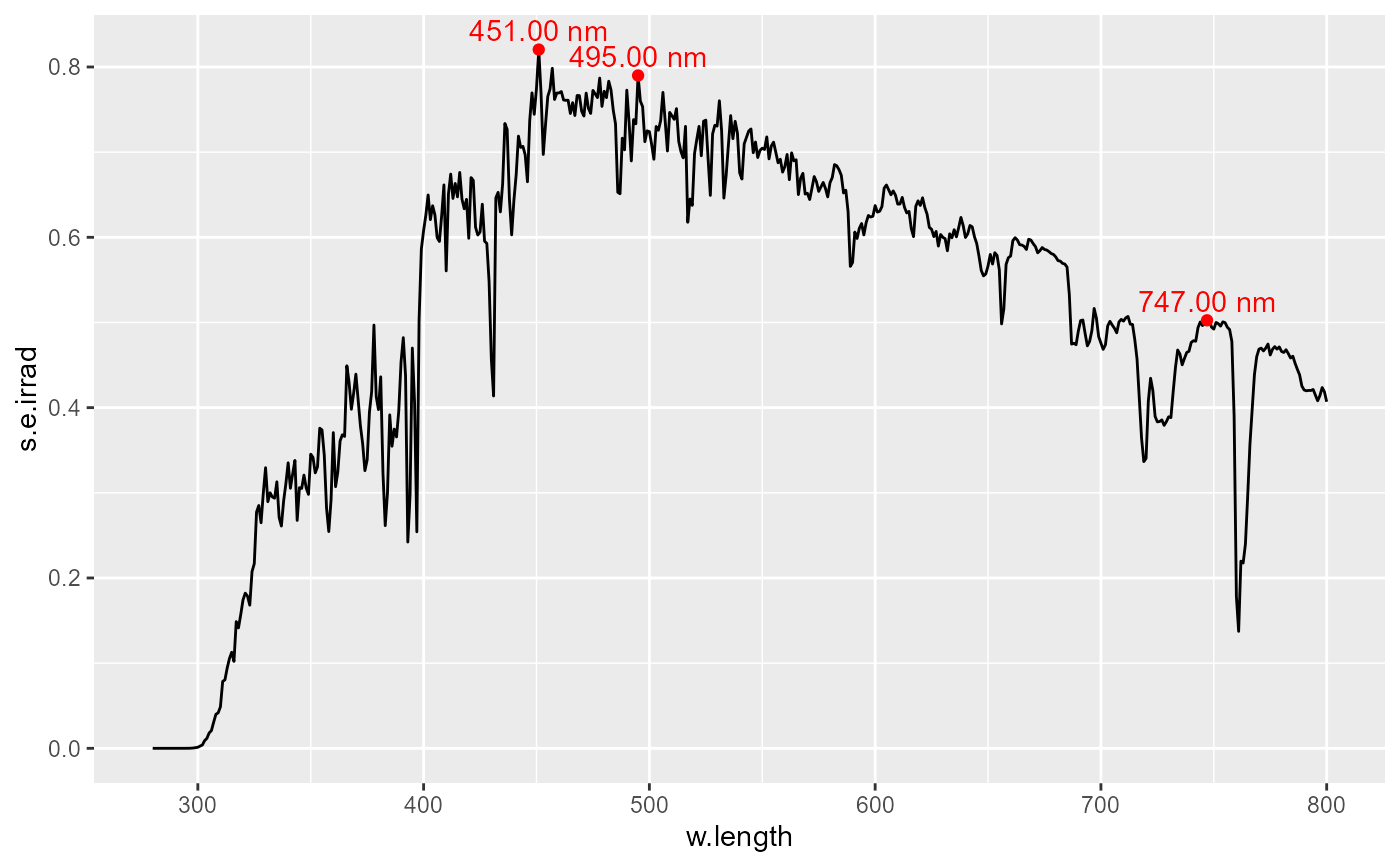 # labels for local fitted peaks
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(span = 51, geom = "point", colour = "red", refine.wl = TRUE) +
stat_peaks(span = 51, geom = "text", colour = "red",
vjust = -0.4, label.fmt = "%3.2f nm",
refine.wl = TRUE)
# labels for local fitted peaks
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(span = 51, geom = "point", colour = "red", refine.wl = TRUE) +
stat_peaks(span = 51, geom = "text", colour = "red",
vjust = -0.4, label.fmt = "%3.2f nm",
refine.wl = TRUE)
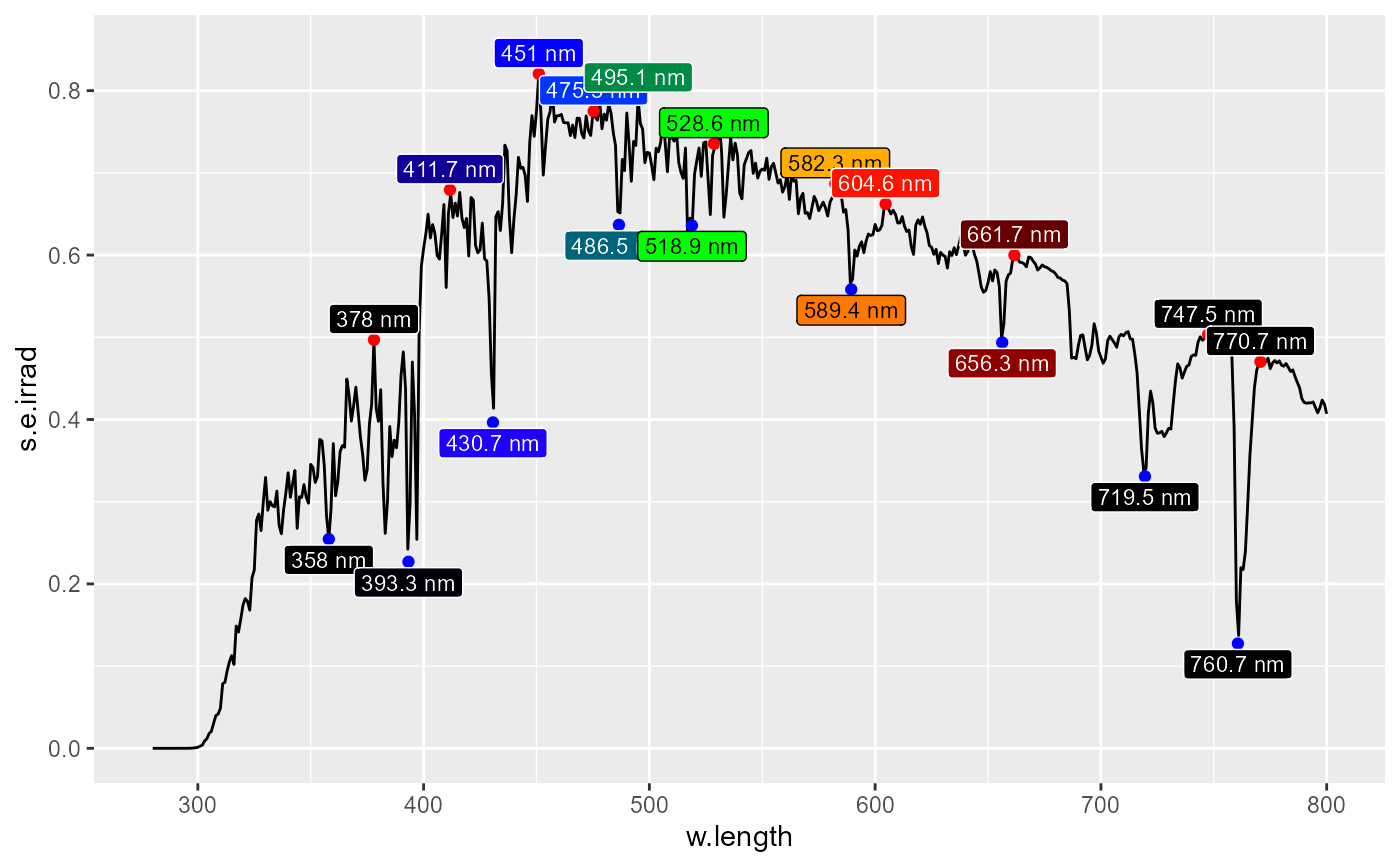
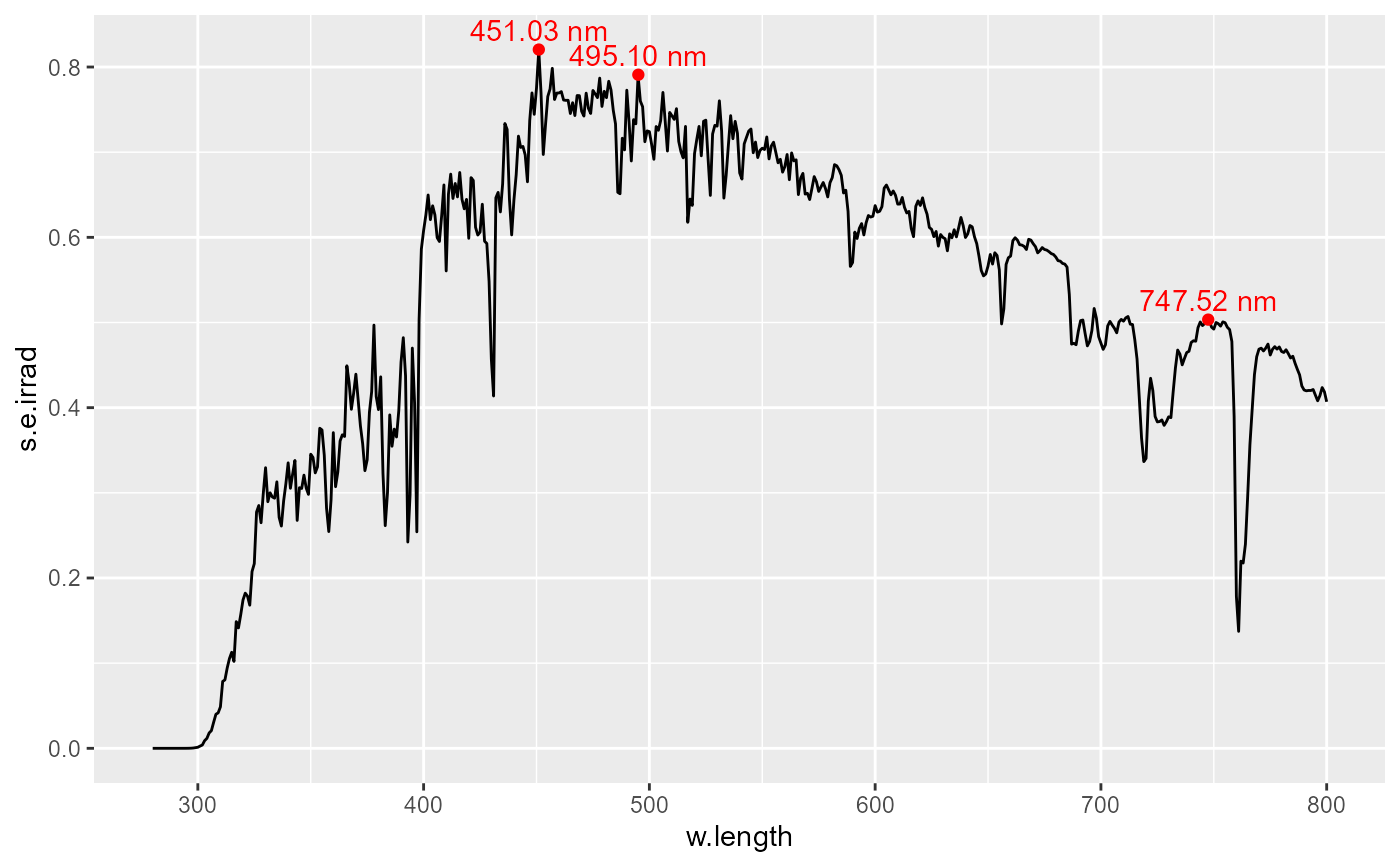 # fitted peaks and valleys
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(span = 31, geom = "point", colour = "red", refine.wl = TRUE) +
stat_peaks(mapping = aes(fill = after_stat(wl.colour), color = after_stat(BW.colour)),
span = 31, geom = "label",
size = 3, vjust = -0.2, label.fmt = "%.4g nm",
refine.wl = TRUE) +
stat_valleys(span = 51, geom = "point", colour = "blue", refine.wl = TRUE) +
stat_valleys(mapping = aes(fill = after_stat(wl.colour), color = after_stat(BW.colour)),
span = 51, geom = "label",
size = 3, vjust = 1.2, label.fmt = "%.4g nm",
refine.wl = TRUE) +
expand_limits(y = 0.85) + # make room for label
scale_fill_identity() +
scale_color_identity()
# fitted peaks and valleys
ggplot(sun.spct) +
geom_line() +
stat_peaks(span = 31, geom = "point", colour = "red", refine.wl = TRUE) +
stat_peaks(mapping = aes(fill = after_stat(wl.colour), color = after_stat(BW.colour)),
span = 31, geom = "label",
size = 3, vjust = -0.2, label.fmt = "%.4g nm",
refine.wl = TRUE) +
stat_valleys(span = 51, geom = "point", colour = "blue", refine.wl = TRUE) +
stat_valleys(mapping = aes(fill = after_stat(wl.colour), color = after_stat(BW.colour)),
span = 51, geom = "label",
size = 3, vjust = 1.2, label.fmt = "%.4g nm",
refine.wl = TRUE) +
expand_limits(y = 0.85) + # make room for label
scale_fill_identity() +
scale_color_identity()